AMD Radeon RX 5600 XT video accelerator Review

Radeon RX 5600 XT Reference Video Card Specifications |
|
|---|---|
| Core Frequency (Gaming / Peak) | 1375/1560 (1615/1750) MHz |
| Number of universal processors | 2304 |
| The number of texture units | 144 |
| Number of Blending Blocks | 64 |
| Effective memory frequency | 12 (14) GHz |
| Memory type | Gddr6 |
| Memory bus | 192-bit |
| Memory size | 6 GigaByte |
| Memory bandwidth | 288 GB / s |
| Computing Performance (FP16) | up to 14.4 teraflops |
| Computing Performance (FP32) | up to 7.2 teraflops |
| Theoretical maximum fill speed | 100 gigapixels / s |
| Theoretical texture sampling rate | 225 gigapixels / s |
| Tire | PCI Express 4.0 |
| Connectors | model dependent |
| power usage | up to 150 (160) W |
| Supplementary Nutrition | model dependent |
| Recommended price $ | $ 279 |
Performance Preview
Graphics card model |
Radeon RX 5600 XT |
Radeon RX 5500 XT |
Radeon RX 5700 |
Radeon RX 480 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPU name | Navi 10 | Navi 14 | Navi 10 | Polaris 10 |
| Architecture | RDNA | RDNA | RDNA | Gcn |
| Process technology, nm | 7 | 7 | 7 | 14 |
| Number of transistors, million | 10.3 | 6.4 | 10.3 | 5.7 |
| Chip area, mm2 | 251 | 158 | 251 | 221 |
| CU blocks, pcs | 36 | 22 | 36 | 36 |
| ALU blocks, pcs | 2304 | 1408 | 2304 | 2304 |
| TMU blocks, pcs | 144 | 88 | 144 | 144 |
| ROP blocks, pcs | 64 | 32 | 64 | 32 |
| Base frequency, MHz | 1607 | 1465 | 1120 | |
| Game frequency, MHz | 1375 (1615) | 1717 | 1625 | – |
| Turbo Frequency, MHz | 1560 (1750) | 1845 | 1725 | 1266 |
| FP32-performance, teraflops | 7.2 | 5.2 | 7.95 | 5.8 |
| Memory type | Gddr6 | Gddr6 | Gddr6 | Gddr5 |
| The amount of memory GB | 6 | 4/8 | 8 | 4/8 |
| Memory frequency, GHz | 12 (14) | 14 | 14 | 7-8 |
| Memory bus width, bit | 192 | 128 | 256 | 256 |
| Power consumption, W | 150 (160) | 130 | 180 | 150 |
| Price at the announcement, $ | 279 | 169/199 | 349 | 199/229 |
AMD experts set the power consumption level of the video card (total board power – TBP, the power of the entire board, and not just one GPU) to 150 (160) watts, which is quite logical for the stripped-down Navi 10 chip.
Although the typical power consumption level is noticeably lower than that of Radeon RX 5700, I would like even less value (however, even the RX 5500 XT is not far away). So the energy efficiency of the younger model should be approximately the same as that of related GPUs. We pass on to the tests, so far from AMD itself:
Architecture features
Over the past year, AMD has released many products manufactured using the 7 nm process technology, and Zen 2 CPUs have become particularly successful, but GPUs based on the new RDNA architecture have also improved the company’s market position.
First, a series for enthusiasts of the Radeon RX 5700 came out of a pair of models that did not differ very much in speed, and at the very end of the year, it came to the budget Radeon RX 5500 video cards. But there was still a rather serious gap between them in terms of performance and price, and finally released today, the model Radeon RX 5600 XT just should fill this niche.

The novelty fills the price range with a price of less than $ 300, and this video card is the next solution, well suited for upgrading obsolete video cards that are installed in gaming systems. According to analysts and Steam statistics, at the end of 2019, more than 20 million monitors manufactured since 2016 have Full HD resolution – the most common now, and the three most popular GPUs in gaming systems are models three years old or older.
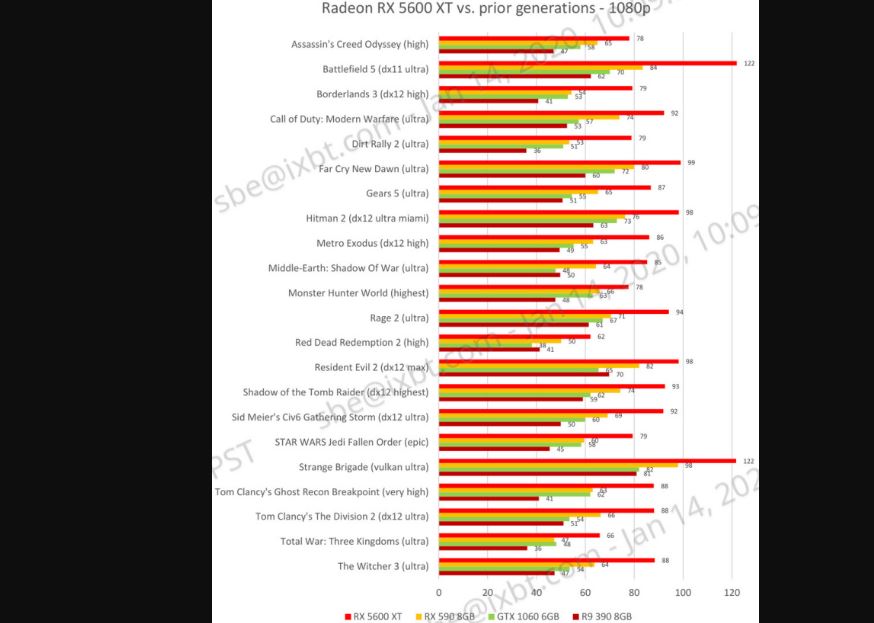
The most common and previously popular video card models, such as the GeForce GTX 1060 and Radeon RX 480, now no longer provide acceptable performance in Full HD resolution with ultra-settings in modern games such as Call of Duty: Modern Warfare, The Division 2, Gears of War 5, The Witcher 3 and many others. And in e-sports projects like Apex Legends and Fortnite, their use does not give 90 FPS, which are highly desirable for high smoothness and accuracy.
That is why AMD also considered it important to release a solution in the coming year, providing 60 FPS and more in the most modern and demanding single-user projects,
Architecture features
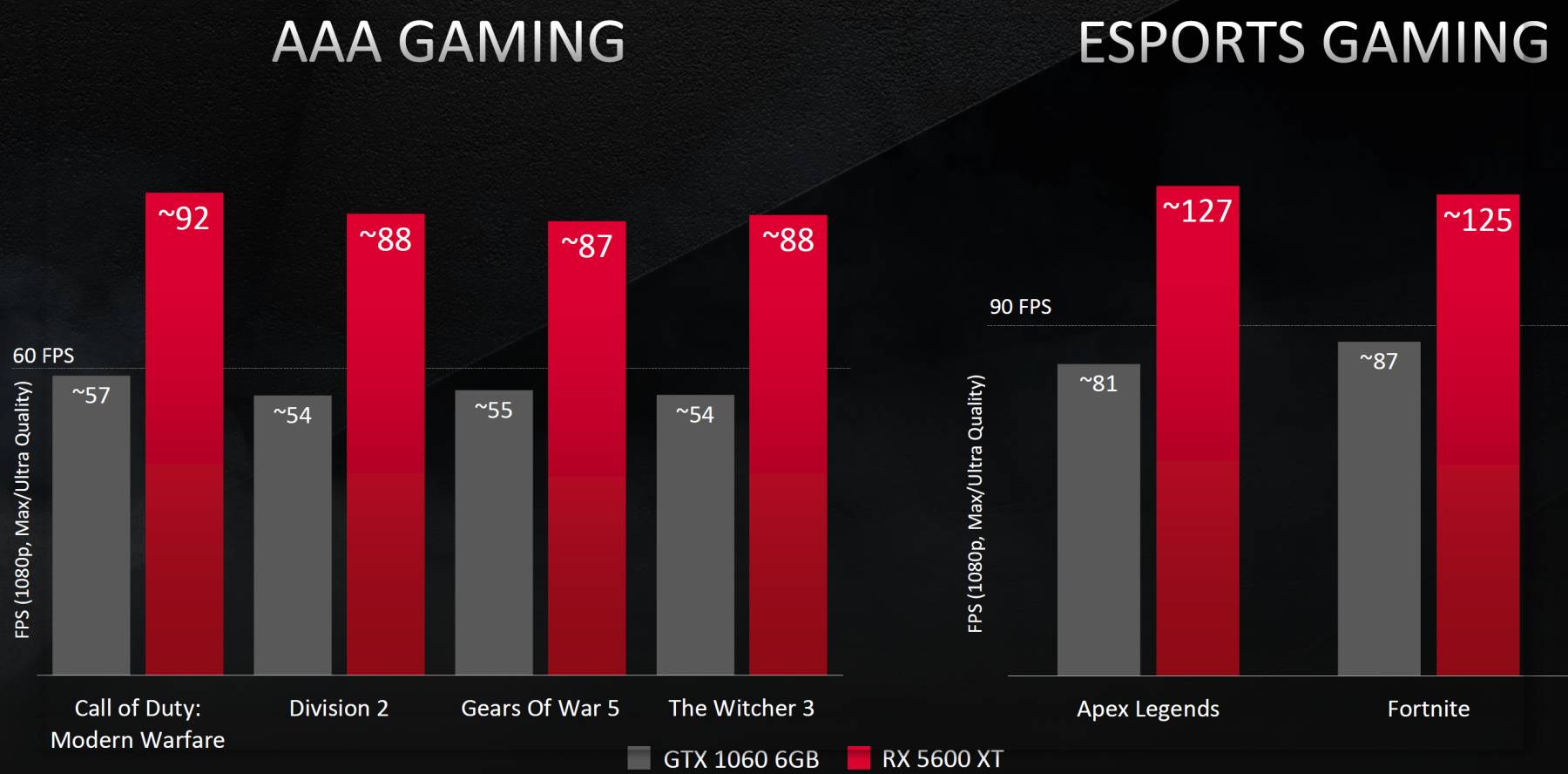
In any case, it is clearly seen that according to AMD, such an upgrade should provide an increase of about 55% on average, and sometimes more. In single-player games, instead of 55 FPS (which is below the generally accepted comfort margin of 60 FPS), players will receive 80-90 FPS, and in e-sports projects – more than 120 FPS, which also goes well with the capabilities of modern gaming monitors with a high refresh rate.
If we compare the new Radeon with modern GeForce, then their advantage over the GTX 1660 Ti and GTX 1660 Super should be 5% -30% (according to AMD, do not forget).
Well, in addition to pure performance, all modern AMD solutions also offer software features that increase performance and reduce latency in some conditions: Radeon Boost and Radeon Anti-Lag, which also help players achieve better results. In general, the company now offers almost an entire line of GPUs, which lacks perhaps the most productive solutions:

The Radeon RX 5500 family is designed to play in Full HD with high settings, video card models have a memory bandwidth of up to 224 GB / s and, according to AMD, they outperform the GeForce GTX 1650 Super on average. The Radeon RX 5600 series has almost a third larger memory bandwidth and will play in the same resolution of 1920 × 1080 with maximum settings and a high frame rate. These solutions are also faster than the GTX 1660 Ti and 1660 Super on average, according to AMD.
The Radeon RX 5500 family
Well, a pair of Radeon RX 5700 has even more than 50% more memory bandwidth and is designed to play in a resolution of 2560 × 1440 pixels. The younger RX 5700 is supposedly faster than the RTX 2060, and the older RX 5700 XT outperforms the RTX 2070 “on average in selected games.” But what to do for fans of Radeon video cards with 4K monitors until the release of the “big Navi” has not yet been reported. Probably continue to play on Radeon VII almost a year ago.
The launch of the Radeon RX 5600 series on the market again took place in two stages. It was decided to announce the exact specifications and recommended price at the beginning of January at CES 2020, but the date of lifting the embargo for reviews and the very decision to enter the market has been postponed until today.
It is understandable that Nvidia did not leave its competitor alone, reducing the price of the weakest GPU with ray tracing support – the GeForce RTX 2060, which became only slightly more expensive than the new Radeon RX 5600 XT, which pretty much spoiled its potential attractiveness. But AMD immediately came up with the answer, which we will discuss later.
The basis of the video card model we are considering today is the well-known Navi 10 graphics processor based on the RDNA architecture, which is closely connected with the latest generation of GCNs. And before reading the article, it will be useful to familiarize yourself with our previous materials on AMD video cards:
Radeon RX 5600 Series Graphics Accelerators |
|
|---|---|
| Chip codename | Navi 10 |
| Production technology | 7 nm |
| Number of transistors | 10.3 billion |
| Core area | 251 mm² |
| Architecture | unified, with an array of processors for streaming processing of any kind of data: vertices, pixels, etc. |
| DirectX hardware support | DirectX 12, with support for Feature Level 12_1 |
| Memory bus | 192-bit memory bus supporting GDDR6 standard |
| CPU Frequency (Gaming / Peak) | 1375/1560 (1615/1750) MHz |
| Computing Blocks | 36 CU computing units (out of 40 physical), consisting of a total of 2304 ALUs (out of 2560) for integer and floating-point calculations (formats INT4, INT8, INT16, FP16, FP32 and FP64 are supported) |
| Texturing blocks | 144 blocks (out of 160) of texture addressing and filtering with support for FP16 / FP32 components and support for trilinear and anisotropic filtering for all texture formats |
| Raster Operations Blocks (ROP) | 64 ROP blocks with support for smoothing modes with the possibility of programmable sampling of more than 16 samples per pixel, including with FP16 or FP32 frame buffer format. |
| Monitor support | support for up to six monitors connected via DVI, HDMI 2.0b and DisplayPort 1.4 |
Card Features
PowerColor Red Devil Radeon RX 5600 XT 6 GB 192-bit GDDR6 |
|
|---|---|
| GPU | Radeon RX 5600 XT |
| Architecture | AMD Navi10 |
| Interface | PCI Express x16 |
| GPU frequency (ROPs), MHz | 1375-1530 (Boost) —1610 (Max) with the new BIOS * : 1530-1610 (Boost) —1750 (Max) |
| Memory frequency (physical (effective)), MHz | 3000 (12000) with the new BIOS *: 3500 (14000) |
| Memory bus width, bit | 192 |
| The number of processing units in the GPU | 36 |
| The number of operations (ALU) in the block | 64 |
| Total number of ALUs | 2304 |
| Number of texture units (BLF / TLF / ANIS) | 108 |
| The number of rasterization blocks (ROP) | 64 |
| Number of Ray Tracing Blocks | – |
| The number of tensor blocks | – |
| Sizes, mm | 240 × 115 × 52 |
| The number of slots in the system unit occupied by the video card | 3 |
| PCB colour | the black |
| Peak power consumption in 3D, W | 157 with the new BIOS *: 164 |
| 2D power consumption, W | 22 |
| Power consumption in sleep mode, W | 3 |
| The noise level in 3D (maximum load), dBA | 18.8 |
| The noise level in 2D (video viewing), dBA | 18.0 |
| The noise level in 2D (in idle), dBA | 18.0 |
| Video outputs | 1 × HDMI 2.0b, 3 × DisplayPort 1.4 |
| Multiprocessor Support | not |
| Maximum number of receivers/monitors for simultaneous image output | 4 |
| Power: 8-pin connectors | 1 |
| Power: 6-pin connectors | 1 |
| Maximum Resolution / Frequency, Display Port | 3840 × 2160 @ 120 Hz (7680 × 4320 @ 30 Hz) |
| Maximum Resolution / Frequency, HDMI | 3840 × 2160 @ 60 Hz |
| Maximum Resolution / Frequency, Dual-Link DVI | 2560 × 1600 @ 60 Hz (1920 × 1200 @ 120 Hz) |
| Maximum Resolution / Frequency, Single-Link DVI | 1920 × 1200 @ 60 Hz (1280 × 1024 @ 85 Hz) |
| Recommended retail price | $ 349 |









