Hantavirus confirmed death! Another new coronavirus?

China: Experts in this article: Yang Chao, MD, Attending Physician of Rocket Army Medical Center
The reviewer of this article: Chen Haixu, Ph.D. in Regenerative Medicine, Associate Researcher, Second Medical Center of PLA General Hospital
A few days ago, the news about the “death of a migrant worker from Hantavirus who had chartered a car through the Ningshan-Shaanxi service area of Beijing-Kunming Expressway” was on the headlines of major media, causing a lot of attention.
On the evening of the 23rd, Ningshan County, Shaanxi Province made a briefing on the incident.
The content showed that a migrant worker died of illness while returning to work through the Ningshan service area of the Beijing-Kunming Expressway. The test results showed that the deceased Tianmou Hantavirus (hemorrhagic fever) nucleic acid test was positive, and all the other 29 people in the same car were implemented on-site Medical observation measures.
During the epidemic, the news came out, causing panic among many netizens. Is this a new type of virus?
First tell everyone: don’t panic! Epidemic hemorrhagic fever can be prevented! Curable! There is a vaccine!
So what kind of disease is this? How is it spread? How to prevent it? Let’s see it together.
What is an epidemic hemorrhagic fever?
Epidemic hemorrhagic fever, also known as renal syndrome hemorrhagic fever, is an acute infectious disease caused by the Bunyavirus Cohantan virus and is a natural epidemic disease. The Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases stipulates that it belongs to the category of Class B infectious diseases.
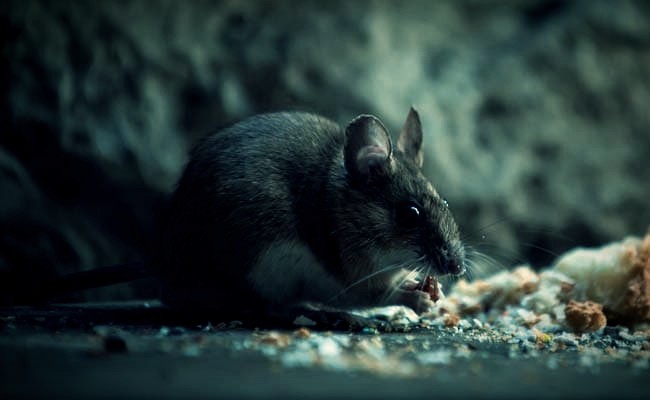
Where is the main source of the Hantavirus?
Hantavirus is an RNA-borne virus that is mainly transmitted by rodents such as rodents and is an RNA virus that spreads all over the world. It is mainly found in saliva, urine, and feces of rodents such as rats.
At present, the Hantaan virus (HTNV) and Seoul virus (SEOV) are prevalent in China. Hantaan virus is stronger than the Seoul virus in terms of virus toxicity.
However, the virus has low resistance to the external environment. Heating, 75% alcohol concentration, etc. can inactivate the virus.
How is a person infected?
House rodents, wild rats and other small rodents are the main host and source of infection for epidemic hemorrhagic fever. Rat-to-human transmission is the main mode of human infection. There are several ways of transmission:
1. Respiratory transmission: Inhaled by aerosols contaminated with the virus in the air.
2. Digestive tract transmission: Infection occurs when eating food or water contaminated with fecal rat feces.
3. Direct contact: The rats were bitten by the virus directly or the patient’s skin and skin mucous membrane were damaged. The wounded mouth directly contacted the poisoned rats’ secretions and excreta and caused the infection.
4. Insect-borne: Various types of parasitic mites that exist on the surface of rodents can cause infections after they bite the human body.
5. Vertical transmission: Studies have shown that the virus can be transmitted to the fetus and fetus through the placenta.
Which people are vulnerable?
It is generally believed that the population is generally susceptible, that is, everyone can be infected with the epidemic hemorrhagic fever-related virus, but the incidence mainly depends on people’s living and working habits, such as wild exploration, tourism, farming, and the habits of rodents.
Male young farmers and workers have a high incidence of disease, but they have longer-lasting immunity after an illness.
What are the symptoms of this disease?
The virus usually incubates in patients for 2 to 3 weeks.
The patient has an acute onset, but the initial symptoms are very similar to the cold, mainly manifesting as fever, headache, sore throat, cough, runny nose, etc., which is easily confused with the cold. It is easy to be misdiagnosed clinically and delay treatment, a 20% -90% Fatality rate.
Then the typical symptoms appear, namely “three pains” (headache, low back pain, orbital pain), “three reds” (redness of the face, neck and upper chest), conjunctival hemorrhage, hyperemia, hypotension shock, and other symptoms. The virus invades the kidneys and can cause renal failure.
What areas are high in China?
Epidemic hemorrhagic fever is long-standing in nature. The uneven distribution of rodents determines the uneven distribution of population incidence in different regions, and the regional distribution of host animals can change with conditions such as food and temperature, so the distribution of endemic areas has variability and relative stability.
The flow report shows that the distribution of epidemic hemorrhagic fever cases is highly dispersed and relatively concentrated, with a high incidence in Shaanxi, Heilongjiang, Shandong, Liaoning, and Jilin. (Data source: Epidemiological analysis of epidemic hemorrhagic fever in China from 2008 to 2012)
Epidemic hemorrhagic fever can occur in all seasons, but usually, the peak in spring and autumn and winter, and the peak in autumn and winter is much higher than the peak in spring.
How should it be scientifically prevented?
1. Anti-rat and anti-rat is the key
Keep proper daily diet, clean up domestic garbage in time, and cut off transmission channels.
Relevant departments implement real-time monitoring of rodent density, clear areas where rodents reproduce and inhabit, scientifically kill rodents, and eliminate sources of infection.
2. Increase protection awareness
During outdoor labor work, do not directly contact the rats to avoid skin damage. If the skin is damaged, immediately disinfect and bandage to avoid contact with the source of infection.
Do a good job of food hygiene and food preservation, and it is forbidden to eat food damaged by rats.
3. Vaccination
Vaccination can effectively prevent epidemic hemorrhagic fever, and it is the most effective measure for individuals to prevent viral hemorrhagic fever. Especially in areas with a high incidence of epidemic hemorrhagic fever, the vaccine protection rate can reach 95%.
If there is an unexplained fever, a history of contact with rats, or eating food contaminated by rats, you should avoid fluke and go to the hospital in time for early detection, early diagnosis, and early treatment.
In summary, we need not be too panicky about this incident. Usually, pay attention to raise awareness of protection and develop good habits.
Also Read:
New coronavirus will damage male reproductive function?
Clinical evidence first appeared! New coronavirus damages male reproductive function
Intel processor exposes new vulnerability: Patch performance drops 77%






