Intel processor exposes new vulnerability: Patch performance drops 77%
After the intel defects were exposed, the security error of the Intel processor and AMD processors suddenly increased. In fact, the research was more in-depth, and the new design principles were the same.
In fact, Intel, AMD, ARM, IBM, and other chip companies welcome and support such risk-related security research, helping to improve the security of their own products. And even fund many research projects. The newly exposed LVI vulnerability is a recent typical.
The full name of LVI is Load Value Injection, which means weight value injection. It was first discovered by security research organization BitDefender and reported to Intel on February 10 this year.
It affects most products since the second generation of Intel Sandy Bridge Core, only Cascade Lake’s second generation can be extended to Xeon, Coffee Lake nine generation Core Comet Lake tenth generation Core partially immune, Ice Lake tenth generation Core completely immune.
The vulnerability may be allowed the attacker to ignore the Intel SGX software protection extension method. The vulnerability also allows us to steals sensitive information from a processor like a ghost threat. But Intel and BitDefender believe it only The ideological attack is likely and is not significant. The risk does not have a substantial threat for the time being.
Intel said the affected products can avoid this risk only by stopping hyper-threading. However, Intel also updated the SGX platform software and SD development kit to avoid potential security risks. In a nutshell, it added protection to the LFENCE directive before the wall of the affected instruction.
Intel’s previous security patches often affected performance. But the intensity was not high. What will happen this time?
Phoenix found a Xeon E3-1275 v6 (Kick Leak) and tested it in a Linux environment, without branching, loading LFENCE before branch prediction, loading LFENCE before RET instruction, implementing LFENCE after loading, Load LFENCE / RET/branch prediction.
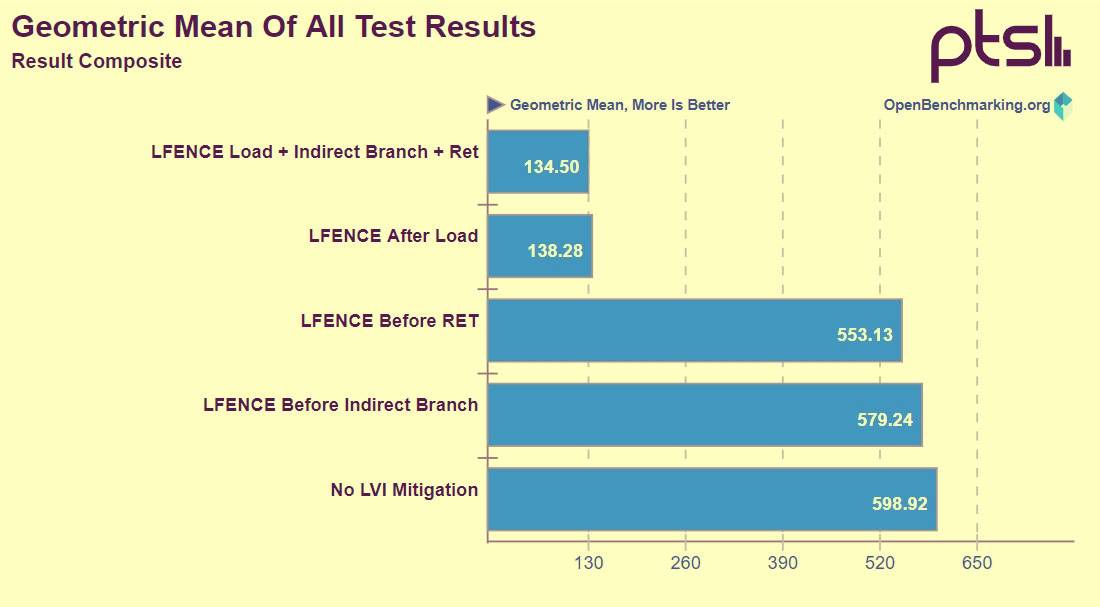
It has been found that loading of LFENCE had little effect before branch prediction and RET instruction, with only 3% and 8% performance loss. But in the latter two cases, there was a significant loss of 77%.
It does not return to ancient society overnight before returning to freedom …
Fortunately, the downside of LVI can be said to have almost no effect on ordinary users. As mainstream PCs do not use SGX at all. Enterprise users need to pay attention to this as they often use SGX and virtualization.
Fortunately, this risk is extremely complicated to exploit. In theory, attacks can be triggered via JavaScript, but this is extremely difficult.
Also Read:
Important discovery! New coronavirus transmitted in Italy on January 1
Wuhan University Experts Find Increasing Causes of New coronavirus Pneumonia Death
Eco-friendly girl Greta Thunberg claims to have new coronavirus pneumonia but says he has recovered






